Mental Health of Older Adults: Ensuring Emotional Well-being in the Golden Years
- Key Facts
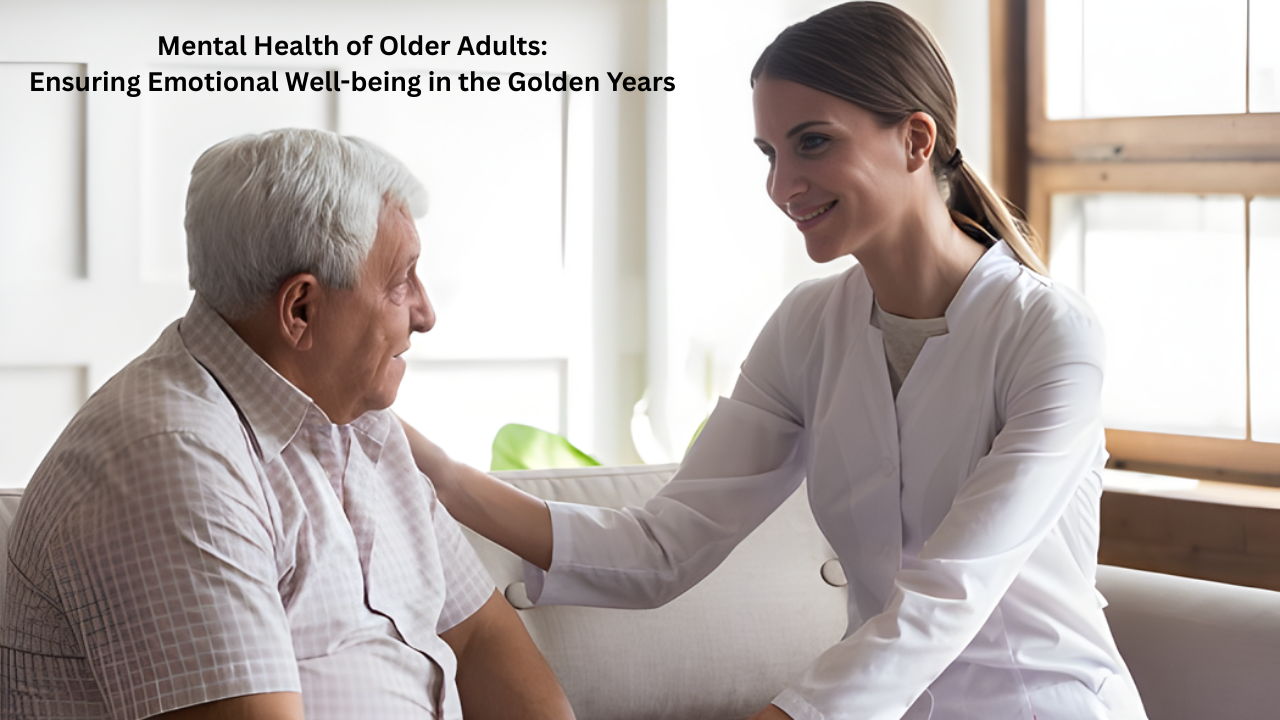
- Mental health is just as important in older age as it is at any other time of life.
- Around 15% of adults aged 60 and over suffer from a mental disorder.
- Common conditions include depression, anxiety, dementia, and substance use disorders.
- Many older adults face social isolation, physical health issues, and reduced independence, which can negatively affect mental well-being.
- Despite the prevalence, mental health issues in older adults are often underdiagnosed and undertreated.
- Overview
As people age, they experience multiple physical, emotional, and social changes. While many adapt well, others may struggle with loneliness, grief, or chronic illness. Mental health conditions in older adults are not a natural part of ageing but are treatable medical conditions that deserve attention and care. Promoting mental well-being among the elderly improves their quality of life, functional independence, and longevity.
- Prevalence
- Depression affects approximately 7% of the world’s older population.
- Anxiety disorders occur in about 3–5% of older adults.
- Dementia affects over 55 million people globally, with nearly 10 million new cases every year.
- Rates of suicide are highest among older adults compared to younger age groups.
- Risk Factors
- Biological: Chronic illnesses, neurodegenerative diseases, medication side effects.
- Psychological: Loss of loved ones, poor coping mechanisms, unresolved trauma.
- Social: Loneliness, isolation, financial stress, elder abuse, or neglect.
- Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity, poor nutrition, substance misuse, and limited social engagement.
- Promotion and Prevention
- Stay socially connected: Encourage interactions with family, friends, and community groups.
- Promote physical activity: Regular exercise improves both mood and cognitive health.
- Balanced nutrition: Adequate diet supports brain and body function.
- Routine screening: Early identification of depression or cognitive decline is essential.
- Community programs: Supportive environments and awareness campaigns can reduce stigma and enhance mental wellness.
- Treatment and Care
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and supportive counseling are effective for late-life depression and anxiety.
- Medications: Antidepressants, anxiolytics, and antipsychotics may be prescribed with caution and regular monitoring.
- Family involvement: Caregiver education and family therapy improve treatment adherence.
- Holistic approach: Combining medical, psychological, and social support yields the best outcomes.
- Geriatric psychiatry services: Specialized care ensures tailored management of coexisting medical and psychological conditions.
- WHO Response
The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes integrating mental health care into primary health systems. Key strategies include:
- Strengthening community-based mental health services.
- Training healthcare workers to recognize and manage geriatric mental health issues.
- Developing age-friendly policies that promote social inclusion.
- Raising global awareness about the importance of mental well-being in older adults.
Conclusion:
Addressing the mental health needs of older adults is essential for a healthy ageing society. With timely intervention, compassionate care, and community support, older adults can continue to live fulfilling, dignified lives.
—
Dr. Kapil Sharma
Best Psychiatrist in Jaipur